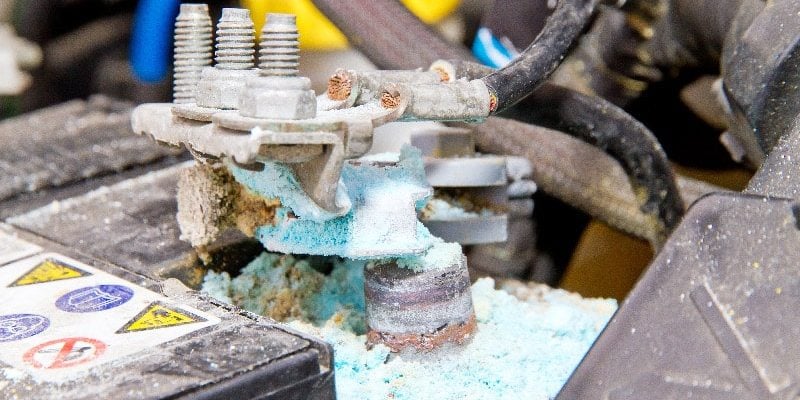
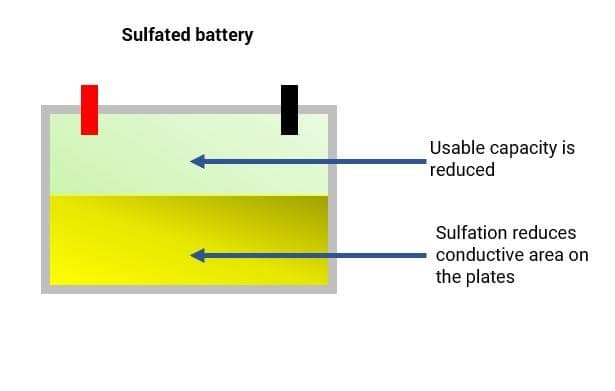
A sulfated battery happens when lead sulfate crystals form on the battery plates. This reduces the battery’s ability to hold a charge.
Batteries are crucial for powering many devices, from cars to electronics. But when a battery becomes sulfated, its efficiency drops. Sulfation is a common issue that can shorten a battery’s life. Understanding what causes sulfation and how to prevent it can save you time and money.
In this blog post, we’ll explain what a sulfated battery is and offer tips to avoid it. We’ll explore the reasons behind sulfation and provide simple steps to keep your battery in good condition. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just someone who wants to maintain their battery, this guide is for you.
Sulfated Battery Basics
Sulfated Battery Basics are essential to understand if you want to maintain your battery’s health and performance. Sulfation is a common problem that affects batteries, particularly lead-acid batteries, and can lead to reduced capacity and lifespan. By understanding what sulfation is and its causes, you can take steps to prevent it and ensure your battery lasts longer.
What Is Sulfation?
Sulfation occurs when lead sulfate crystals form on the battery plates. This happens when a battery is not charged properly. Over time, these crystals harden and become difficult to remove, which impairs the battery’s ability to hold a charge.
Here are some key points about sulfation:
- Lead sulfate crystals: These form naturally during the discharge cycle of a lead-acid battery.
- Reversible vs. irreversible: In its early stages, sulfation can be reversed through proper charging. Once the crystals harden, it becomes irreversible.
- Impact on performance: Sulfation reduces the battery’s capacity, making it less efficient and shortening its lifespan.
To illustrate how sulfation affects a battery, consider the following table:
| Stage | Condition | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|
| Early | Soft lead sulfate crystals | Reversible |
| Advanced | Hard lead sulfate crystals | Irreversible |
Causes Of Sulfation
Several factors contribute to sulfation in batteries. Knowing these causes can help you prevent this issue and maintain your battery’s health.
Here are the main causes of sulfation:
- Undercharging: If a battery is not fully charged, lead sulfate crystals start to form and accumulate on the plates.
- Extended storage: Batteries left unused for long periods tend to sulfate. Regular use and charging can prevent this.
- Low electrolyte levels: Maintaining proper electrolyte levels is crucial. Low levels can expose the battery plates to air, causing sulfation.
- High temperatures: Heat accelerates the formation of lead sulfate crystals. Keeping batteries in cool environments can reduce the risk.
Consider these tips to prevent sulfation:
- Regularly charge your battery to full capacity.
- Avoid leaving the battery unused for long periods.
- Check and maintain proper electrolyte levels.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
By understanding and addressing these causes, you can prolong your battery’s life and performance.

Credit: www.foxtronpowersolutions.com
Signs Of Sulfation
A sulfated battery can cause many problems. It’s important to understand the signs of sulfation to prevent it. In this section, we will discuss the performance issues and visual indicators that suggest a battery is sulfated. Knowing these signs can save time and money.
Performance Issues
A sulfated battery often shows performance issues. These issues can affect the efficiency and lifespan of your battery. Here are some common performance problems:
- Slow Charging: If your battery takes longer to charge, it may be sulfated. This happens because sulfate crystals block the chemical reactions needed for charging.
- Reduced Capacity: A sulfated battery cannot hold as much charge. You may notice that your devices or vehicles need charging more often.
- Frequent Discharging: If your battery discharges quickly, it might be due to sulfation. This means that the battery cannot store energy efficiently.
Performance issues can also be identified through testing. Using a battery tester can provide valuable data:
| Normal Battery | Sulfated Battery |
|---|---|
| Charges quickly | Charges slowly |
| Holds charge well | Low capacity |
| Stable voltage | Unstable voltage |
Identifying performance issues early can help prevent further damage. Regular maintenance and testing are key to ensuring your battery stays in good condition.
Visual Indicators
Visual indicators can also signal a sulfated battery. Inspecting your battery regularly can help you spot these signs early. Here are some common visual indicators:
- White Crystals: White or gray crystals on the battery terminals are a sign of sulfation. These crystals are sulfate deposits that build up over time.
- Corroded Terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can indicate sulfation. Corroded terminals can interfere with the battery’s ability to charge and discharge properly.
- Swollen Battery Case: A swollen or bulging battery case can be a sign of sulfation. This happens because sulfate crystals cause internal pressure.
Visual inspection should be part of regular battery maintenance. Here is a simple checklist for visual inspection:
| Inspection Point | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Battery Terminals | White crystals or corrosion |
| Battery Case | Swelling or bulging |
| Battery Surface | Dirt or residue buildup |
Regular visual checks can help you catch sulfation early. Keeping your battery clean and well-maintained is crucial for its longevity.
Impact On Battery Life
When a battery becomes sulfated, it loses its effectiveness. Sulfation happens when lead sulfate crystals form on the battery plates. This can significantly impact battery life. Understanding how sulfation affects your battery can help you prevent it and maintain your battery’s performance.
Reduced Capacity
A sulfated battery shows a clear reduction in capacity. This means the battery cannot hold as much charge as it should. As lead sulfate crystals build up, they block the chemical reactions needed for the battery to work properly. This leads to several problems:
- The battery charges slowly.
- The battery discharges quickly.
- Devices powered by the battery perform poorly.
For instance, a car battery that is sulfated might struggle to start the engine. Let’s look at the technical aspect of this:
| Battery Condition | Capacity |
|---|---|
| Healthy | 100% |
| Sulfated | 50% or less |
In a healthy battery, the capacity remains close to 100%. But in a sulfated battery, the capacity can drop to 50% or even lower. This drastic reduction impacts the overall performance and usability of the battery.
Shortened Lifespan
A sulfated battery does not last as long as a healthy one. The buildup of lead sulfate crystals can cause permanent damage. This shortens the battery’s lifespan significantly. Here are some signs of a shortened battery lifespan due to sulfation:
- The battery needs frequent recharging.
- The battery fails to hold a charge for a long time.
- The battery shows signs of physical damage, like bulging.
Regular sulfation can make a battery unusable within a few months. In contrast, a well-maintained battery can last several years. The impact of sulfation on lifespan is clear when we compare the expected life of a battery:
| Battery Type | Expected Lifespan (Healthy) | Expected Lifespan (Sulfated) |
|---|---|---|
| Car Battery | 3-5 years | 1-2 years |
| Marine Battery | 4-6 years | 1-3 years |
In summary, preventing sulfation is key to maintaining both the capacity and lifespan of your battery. Understanding these impacts can help you take better care of your batteries.

Credit: www.crownbattery.com
Preventing Sulfation
Introduction paragraph about What Is a Sulfated Battery? Learn How to Prevent It and Preventing Sulfation…
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to preventing battery sulfation. This process occurs when lead sulfate crystals build up on the battery plates, reducing its capacity. To keep your battery in top condition, follow these simple steps:
- Check water levels: Ensure the electrolyte levels are adequate. Use distilled water to top up if needed.
- Clean terminals: Remove any corrosion on the terminals. Use a mix of baking soda and water.
- Inspect for damage: Look for any physical damage to the battery casing or terminals.
- Test voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery’s voltage. It should be between 12.4V and 12.7V for a fully charged battery.
Maintaining a regular check-up schedule helps identify issues before they worsen. Create a monthly maintenance plan. Here’s an example:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check water levels | Monthly |
| Clean terminals | Quarterly |
| Inspect for damage | Monthly |
| Test voltage | Monthly |
Regular maintenance not only extends battery life but also ensures optimal performance. Consistent care can prevent the buildup of harmful sulfate crystals. Keep your battery healthy with these simple tasks.
Proper Charging Techniques
Proper charging techniques are essential to prevent sulfation. Overcharging or undercharging can lead to sulfate buildup. Follow these guidelines to charge your battery correctly:
- Use the right charger: Ensure the charger is suitable for your battery type and capacity.
- Charge at the correct rate: Charging too fast can cause overheating. Charging too slow can lead to sulfation. Refer to the battery’s specifications for the correct rate.
- Avoid deep discharges: Do not let the battery discharge below 20% of its capacity. Deep discharges can cause sulfation.
- Monitor charging time: Do not leave the battery on the charger for too long. Overcharging can damage the battery.
Using a smart charger can help manage these aspects. Smart chargers can adjust the charging rate and prevent overcharging. They can also provide maintenance charging, which keeps the battery at optimal levels without overcharging. Here’s a comparison of manual and smart chargers:
| Feature | Manual Charger | Smart Charger |
|---|---|---|
| Adjustable Charging Rate | No | Yes |
| Prevents Overcharging | No | Yes |
| Maintenance Charging | No | Yes |
Proper charging keeps your battery healthy and prevents sulfation. Following these techniques ensures a longer battery life and better performance. Choose the right charger and follow the guidelines for the best results.
Desulfation Methods
Sulfated batteries are a common issue for many battery users. Sulfation occurs when lead sulfate crystals build up on the battery plates. This can reduce the battery’s efficiency and lifespan. Learning how to prevent sulfation is crucial. One effective way is through desulfation methods. These methods help remove the sulfate crystals and restore battery performance.
Chemical Solutions
Chemical solutions can be effective in desulfating batteries. These solutions dissolve the lead sulfate crystals. There are several types of chemical solutions available:
- Epsom Salt Solution: Mix Epsom salt with distilled water. Add this mixture to the battery cells. Epsom salt helps break down the sulfate crystals.
- EDTA Solution: EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) is a chemical that binds with the sulfate crystals. It converts them into a soluble form. Add the EDTA solution to the battery cells.
- Commercial Desulfators: These are pre-made solutions available in stores. They are designed to dissolve sulfate crystals effectively.
Using these chemical solutions can help restore a sulfated battery. Always follow safety guidelines when handling chemicals. Wear gloves and protective eyewear. Ensure good ventilation in your workspace. Chemical solutions can be a cost-effective way to prolong battery life.
Pulse Charging
Pulse charging is another method to desulfate batteries. This method uses a charger that sends out pulses of electricity. These pulses help break down the sulfate crystals. Pulse charging is effective and less invasive than chemical solutions.
Here are the steps to use pulse charging:
- Connect the pulse charger to the battery.
- Set the charger to the appropriate settings. Refer to the charger’s manual for details.
- Start the charging process. The charger will send pulses of electricity to the battery.
- Monitor the battery’s voltage and condition. The process may take several hours.
Pulse charging has several benefits:
- It is easy to use. Most pulse chargers come with clear instructions.
- It is non-invasive. There is no need to open the battery cells.
- It can extend the battery’s lifespan significantly.
Using a pulse charger can rejuvenate a sulfated battery. It is a safe and effective method for desulfation. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the best results.
Credit: www.power-sonic.com
Choosing The Right Battery
Choosing the right battery is crucial to prevent sulfation and ensure your device runs smoothly. Understanding different types of batteries and their quality can help you make an informed decision.
Types Of Batteries
There are various types of batteries available, each with its own characteristics. Here are some common types:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: These are the most common and affordable. They are used in cars, boats, and motorcycles.
- AGM Batteries: Absorbent Glass Mat batteries are a type of lead-acid battery. They offer better performance and longer life.
- Gel Batteries: These batteries use a gel electrolyte. They are spill-proof and can withstand higher temperatures.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are lightweight and have a high energy density. They are used in laptops, smartphones, and electric vehicles.
Choosing the right type of battery depends on your specific needs. For instance, if you need a battery for a high-performance vehicle, an AGM or Gel battery might be a better choice.
Quality Considerations
The quality of a battery is another important factor to consider. Here are some points to keep in mind:
- Brand Reputation: Choose a well-known brand. They are more likely to offer reliable and durable batteries.
- Warranty: Look for a battery with a good warranty. This can give you peace of mind in case of defects or issues.
- Manufacture Date: Check the manufacture date. Older batteries may not perform as well as newer ones.
- Specifications: Ensure the battery meets the specifications required for your device. This includes voltage, capacity, and size.
Investing in a high-quality battery can save you money and trouble in the long run. A reliable battery will last longer and perform better, reducing the risk of sulfation.
Common Myths
Sulfation is a common issue with lead-acid batteries. It occurs when the lead sulfate crystals harden and reduce the battery’s capacity. Many myths surround sulfated batteries. It’s essential to understand these myths to better care for your battery. Let’s debunk some of the common myths about sulfated batteries.
Sulfation Is Inevitable
Many people believe that sulfation is an unavoidable part of using lead-acid batteries. This is not true. Sulfation can be prevented with proper battery maintenance. Regularly charging your battery and avoiding deep discharges can help.
Here are some tips to prevent sulfation:
- Regular Charging: Charge your battery often. Do not let it sit discharged for long periods.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Do not drain your battery completely before recharging.
- Use a Battery Maintainer: These devices keep your battery charged when not in use.
- Check Electrolyte Levels: Maintain proper electrolyte levels in your battery.
Following these steps can greatly reduce the risk of sulfation. Battery maintenance is the key to a longer battery life and better performance.
Only Old Batteries Sulfate
Another common myth is that only old batteries sulfate. This is false. Even new batteries can sulfate if not properly maintained. Sulfation can occur in any lead-acid battery regardless of its age.
Here are some reasons why new batteries sulfate:
- Poor Maintenance: Neglecting to charge or overcharging a new battery can lead to sulfation.
- Improper Storage: Storing a battery in hot or cold environments can cause sulfation.
- Manufacturing Defects: Sometimes, new batteries have defects that make them more prone to sulfation.
To prevent new batteries from sulfating, follow these steps:
- Charge the battery fully before first use.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place.
- Use a battery maintainer if the battery will not be used for a long time.
- Check for any signs of defects and address them immediately.
Proper care and maintenance are crucial, regardless of the battery’s age. Understanding these myths and taking preventive measures can help you get the most out of your battery.
Future Of Battery Technology
Battery technology is evolving rapidly, bringing new possibilities for energy storage. One significant challenge is sulfation, which can reduce battery life. Understanding sulfated batteries and how to prevent them is crucial. The future of battery technology promises solutions to these issues, enhancing performance and reliability.
Innovations In Battery Design
Innovations in battery design are paving the way for more efficient and longer-lasting batteries. Modern batteries are being designed to minimize sulfation and other common issues. Here are some of the key innovations:
- Advanced Materials: New materials are being used to make batteries more resilient to sulfation. For example, carbon-based materials can help prevent the buildup of lead sulfate crystals.
- Improved Electrolytes: Scientists are developing better electrolytes that reduce the chances of sulfation. These electrolytes can maintain their properties for longer periods, ensuring stable battery performance.
- Smart Battery Management Systems (BMS): Modern batteries come with sophisticated BMS that monitor and regulate the charging and discharging processes. This helps in preventing conditions that lead to sulfation.
Below is a table highlighting some of the latest innovations and their benefits:
| Innovation | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Advanced Materials | Reduced sulfation, longer battery life |
| Improved Electrolytes | Stable performance, reduced maintenance |
| Smart BMS | Prevents overcharging, optimizes battery health |
These innovations are not just theoretical; many are already in use, showing promising results. By incorporating these advancements, batteries can last longer and perform better, providing reliable energy storage solutions.
Sulfation Prevention Advances
Sulfation prevention is a critical area of focus in battery technology. New strategies and technologies are being developed to tackle this issue effectively. Here are some of the recent advances:
- Regular Maintenance: Simple practices like keeping the battery charged and clean can significantly reduce sulfation. Regular check-ups ensure that the battery is functioning correctly.
- Pulsed Charging: This method involves charging the battery with short, high-current pulses. It helps in breaking down lead sulfate crystals, preventing sulfation.
- Desulfation Devices: These devices are designed to remove sulfation from batteries. They send controlled electrical pulses to dissolve the sulfate crystals, restoring battery capacity.
Here’s a table summarizing these advances:
| Advance | Function |
|---|---|
| Regular Maintenance | Prevents buildup of sulfate crystals |
| Pulsed Charging | Breaks down existing sulfate crystals |
| Desulfation Devices | Restores battery capacity by dissolving crystals |
These advances make it easier to maintain battery health and extend their lifespan. By implementing these strategies, users can ensure their batteries remain free from sulfation and perform efficiently over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Prevent Battery Sulfation?
Maintain proper battery charge levels. Use a quality charger with desulfation mode. Avoid deep discharges. Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Regularly check and maintain electrolyte levels.
How Do You Fix A Sulfated Battery?
To fix a sulfated battery, use a desulfation charger. This breaks down lead sulfate crystals. Alternatively, apply a mix of distilled water and Epsom salt. Charge the battery slowly to restore capacity. Always follow safety guidelines during the process.
What Is The Fastest Way To Desulfate A Battery?
The fastest way to desulfate a battery is using a high-frequency pulse charger. This device breaks down sulfate crystals quickly. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safety and effectiveness.
Can You Still Charge A Sulfated Battery?
Yes, you can still charge a sulfated battery. Use a desulfation charger or a high-frequency pulse charger to restore it.
What Is A Sulfated Battery?
A sulfated battery has lead sulfate crystals on its plates, reducing performance.
How Does Sulfation Occur In Batteries?
Sulfation happens when a battery is undercharged, overcharged, or left discharged for long.
Why Is Sulfation Bad For Batteries?
Sulfation reduces battery capacity, lifespan, and efficiency, making it harder to charge.
Conclusion
Preventing sulfation keeps your battery in good condition. Regular maintenance is key. Clean terminals and check voltage often. Use a proper charger to avoid overcharging. Store your battery in a cool, dry place. Understand your battery’s needs for a longer life.
Small steps make a big difference. Keep your battery healthy and efficient. Avoid costly replacements by following these tips. Your battery will thank you.


![How to Clean a Generator Carburetor? – [Easy Steps] for Beginners](https://generatoredge.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/how-to-clean-a-generator-carburetor-2-360x240.webp)